Research
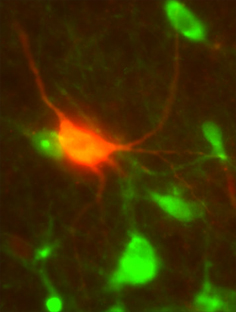
A biocytin-filled neuron co-labeled with choline acetyltransferase in the LDTg

Electrophysiology set-up
Nicotine and ethanol are two of the most widely co-abused drugs. Ethanol is reported to enhance the rewarding effects of cigarette smoking, which may be due to an interaction between ethanol and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) in brain reward pathways. The ventral tegmental area (VTA) receives strong cholinergic and glutamatergic input from the lateral dorsal tegmental nucleus (LDTg), which also contains a high density of cells expressing nAChRs. Ethanol modulates nAChR-mediated currents in cell culture, but no similar studies have been carried out in brain slices. To investigate this interaction, we are testing the effect of bath applied ethanol on nAChR-mediated inward currents induced by focal application of acetylcholine using whole cell patch clamp recording in the LDTg and VTA of adult rats.
- McDaid, J. and McGehee, DS (2009) Ethanol inhibits alpha-7 nicotinic receptors in the laterodorsal tegmentum via a PKA dependent pathway. Soc. for Neuroscience Abstracts 2009 Meeting, Chicago, IL.